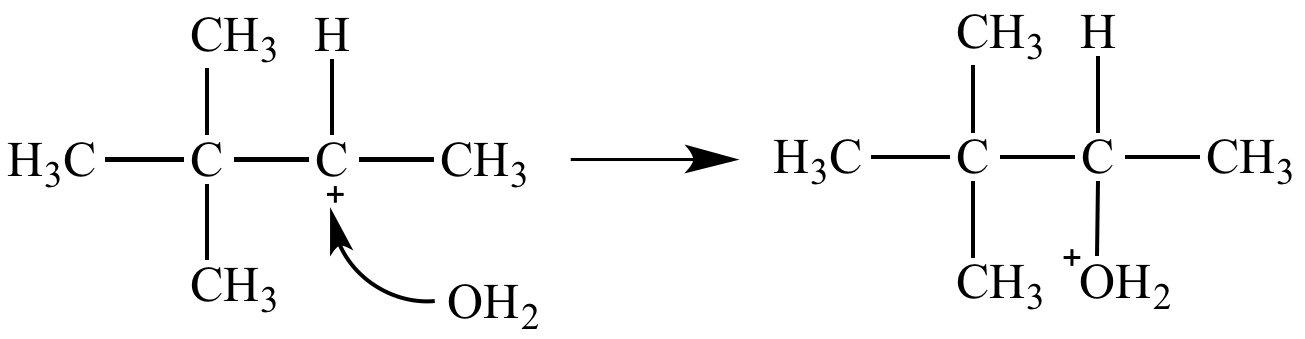
Carbocation fate #1: Capture a nucleophile. In this example a secondary carbocation captures a molecule of water to form an oxonium ion.
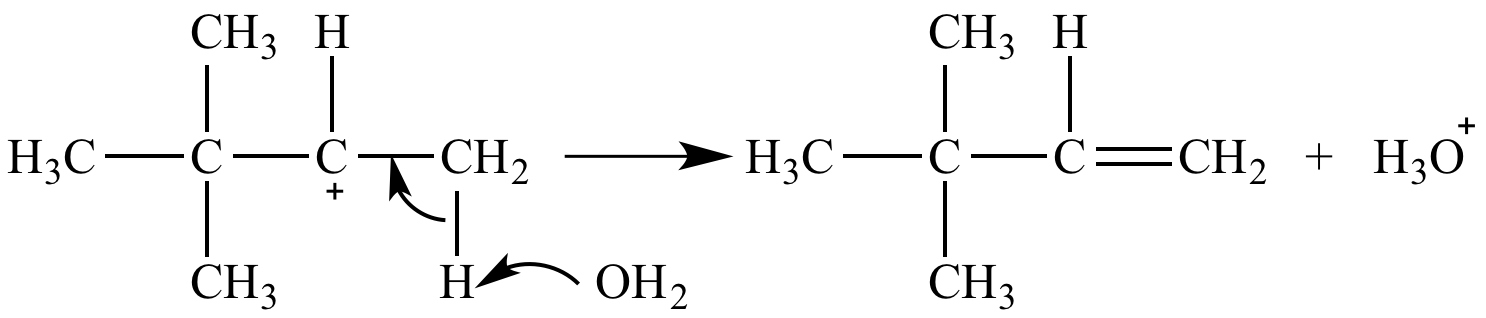
Carbocation fate #2: Be deprotonated to form a pi bond. In this example a secondary carbocation is deprotonated by water to form an alkene and a hydronium ion.
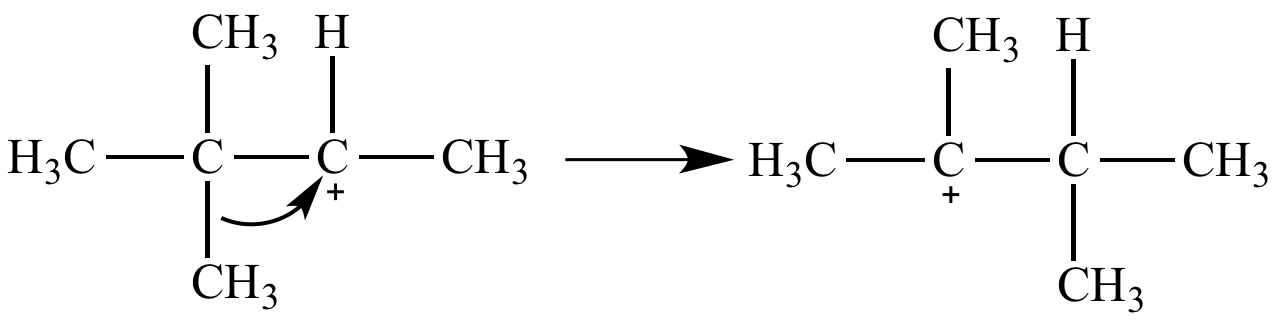
Carbocation fate #3: Rearrangement. In this example a secondary carbocation suffers a 1,2-shift of a methyl group to form a tertiary carbocation. Also called a Wagner-Meerwein shift.