 |
 |
|
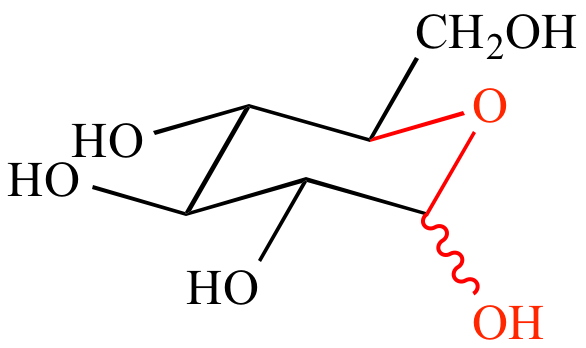
| Glucopyranose |
Acyclic
glucose |
 |
+ |
 |
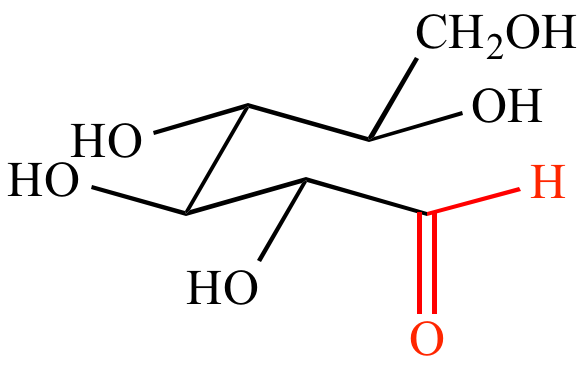
 |
+ |
 |
|
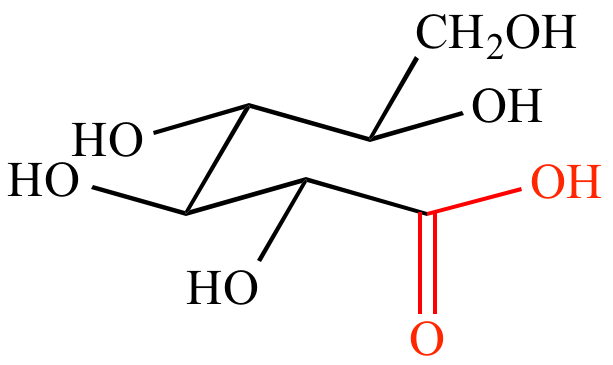
| Acyclic glucose | Benedict's solution | Oxidized glucose | CuO precipitate | |||
| (aqueous Cu2+) |
 |
+ |
 |
No
reaction |
|
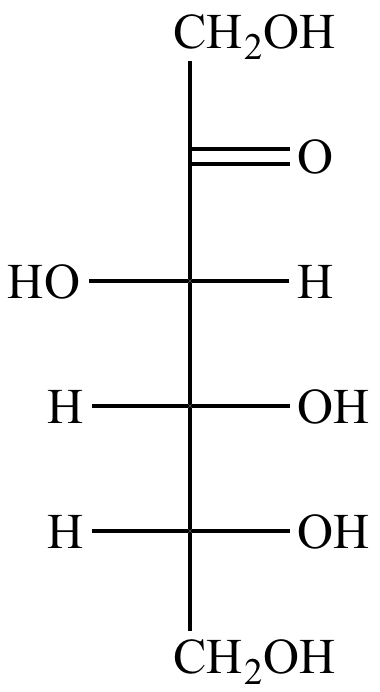
| Fructose |
Benedict's
solution |