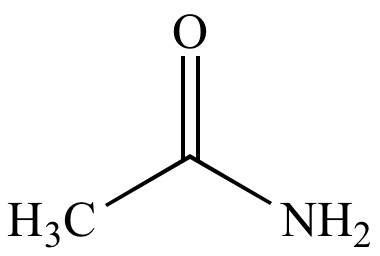
 |
+ |
(CH3)2NH |
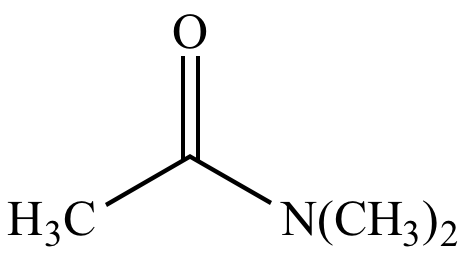 |
+ |
NH3 |
|
| Acetamide |
Dimethylamine |
N,N-dimethylacetamide |
Ammonia |
 |
+ |
(CH3)2NH |
 |
+ |
NH3 |
|
| Acetamide |
Dimethylamine |
N,N-dimethylacetamide |
Ammonia |