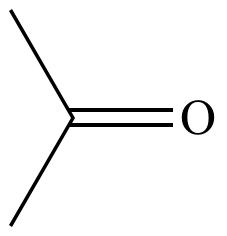
 |
+ |
CH3NH2 |
pTsOH |
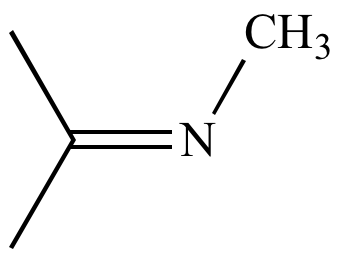 |
NaBH4 |
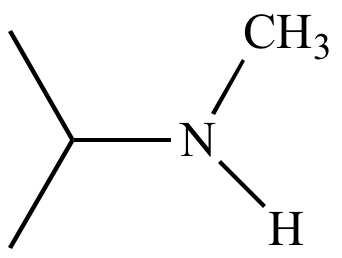 |
| Acetone |
Methylamine |
N-methylpropan-2-imine Reaction intermediate |
Isopropyl
methyl
amine Reaction product |