Ozone
layer: A region in the Earth's atmosphere, at
approximately 20-30 km altitude, containing about 10
ppm ozone.
This ozone
absorbs solar high-energy ultraviolet light, thus protecting
organisms at the Earth's surface from this light's damaging
effects. Chlorofluorocarbons
(CFCs)
and other organic
halides have been implicated in depletion
of the ozone layer, resulting in unnaturally large annual
ozone
holes over the Earth's Antarctic and Arctic regions.
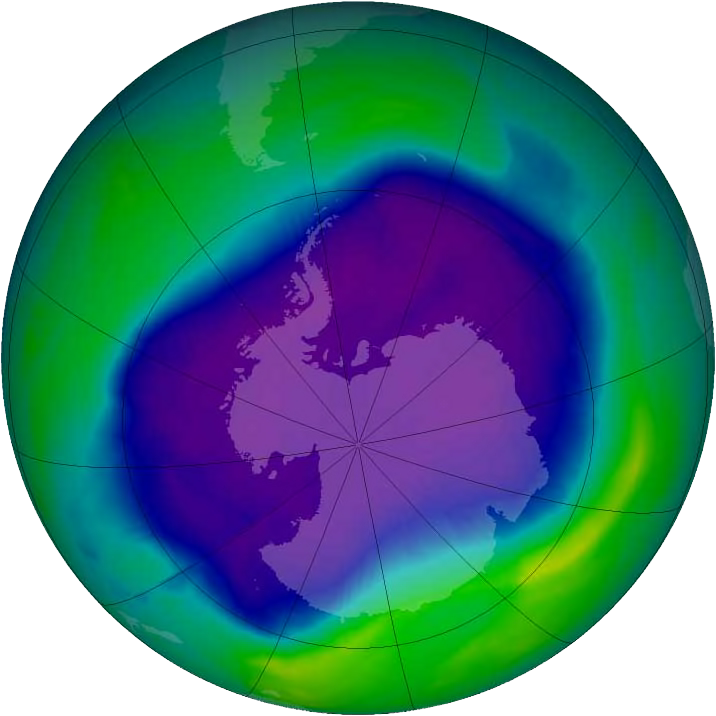
A false color image of the Antarctic ozone
hole, as measured on September 24, 2006. Bluer color =
less ozone;
redder color = more ozone.
At 11.4 million square miles, this was the largest ozone
hole measured to date.