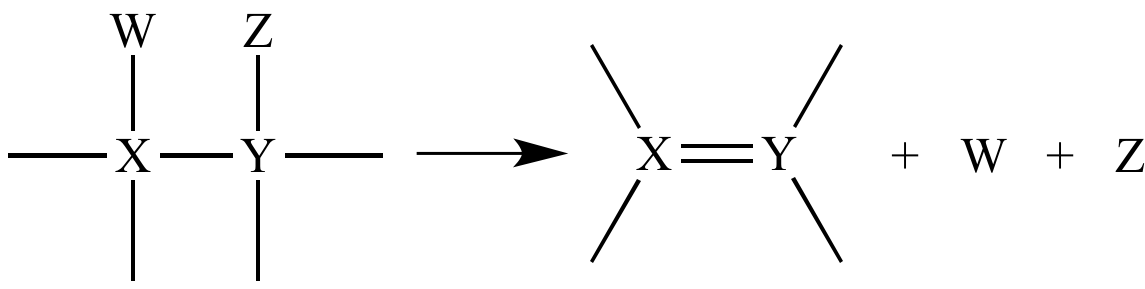
A generalized β-elimination reaction.
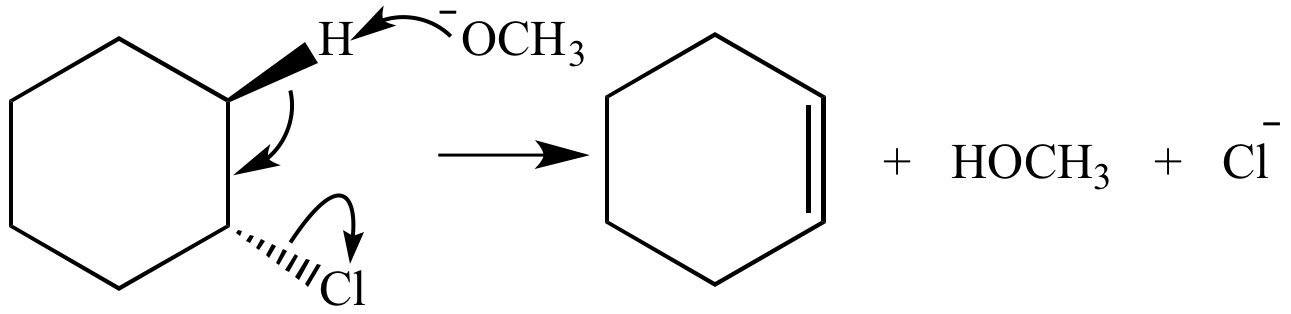
A β-elimination reaction following the E2 mechanism in which a β-hydrogen is removed by methoxide ion (a base). Chloride ion is the leaving group. The product (cyclohexene) is an alkene.
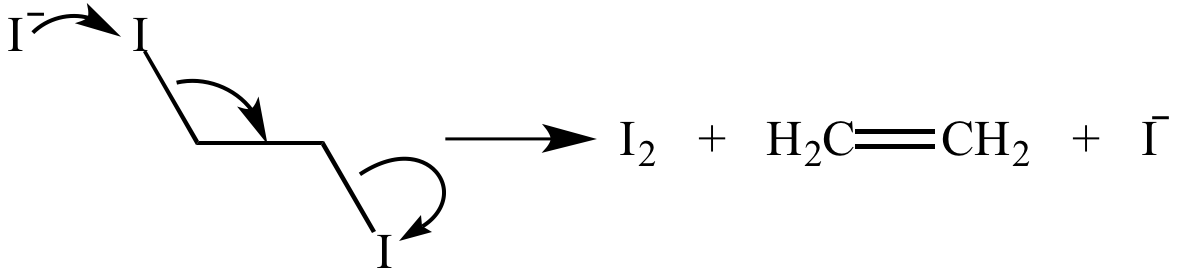
A β-elimination reaction following the E2 mechanism in which an iodine atom is removed by a iodide ion (a nucleophile). A second iodide ion is the leaving group. The product (ethylene) is an alkene.
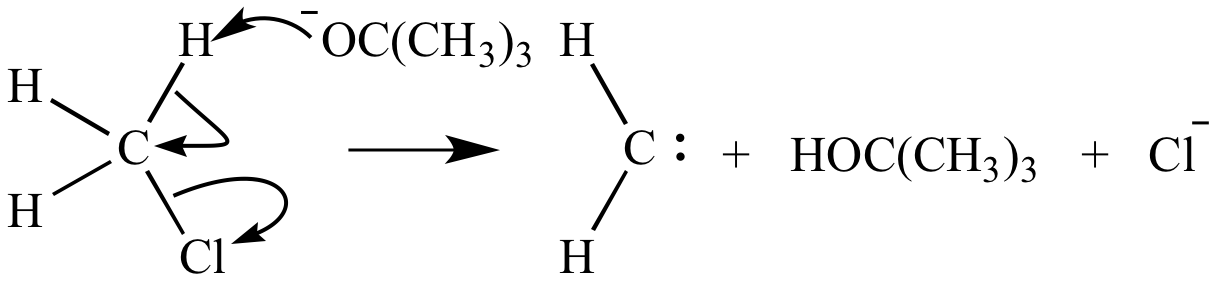
An α-elimination reaction in which the α-hydrogen of chloroform is removed by tert-butoxide ion (a base). Chloride ion is the leaving group. The product is a carbene.